Non-Right-Angled Triangle Trigonometry
In previous chapters, we explored trigonometry in right-angled triangles using sine, cosine, and tangent. However, many real-world problems involve triangles that are not right-angled. To solve these, we use the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines, which apply to any triangle.
Convention for Labelling Triangles: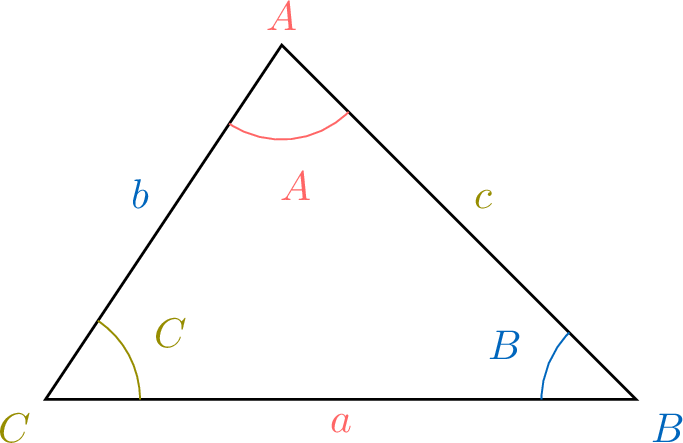
Convention for Labelling Triangles:
- For triangle \(ABC\), the angles at vertices \(A\), \(B\), and \(C\) are labelled \(A\), \(B\), and \(C\) respectively.
- The sides opposite these angles are labelled \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) respectively.

Area of a Triangle Using Two Sides and the Included Angle
When two sides and the included angle of a triangle are known, the area can be calculated using the formula involving the sine of the angle. This is particularly useful in non-right-angled triangles.
Proposition Area Formula
The area of a triangle is:$$\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \textcolor{colordef}{\text{side}} \times \textcolor{colorprop}{\text{side}} \times \sin(\textcolor{olive}{\text{included angle}})$$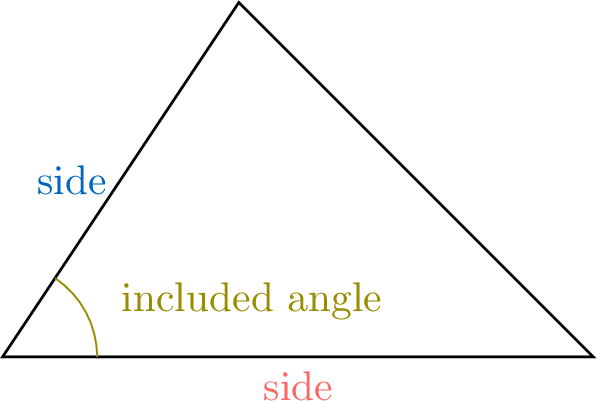

Example
For the triangle 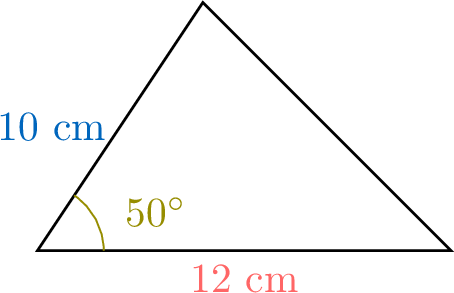 , find the area.
, find the area.
 , find the area.
, find the area.
$$\begin{aligned}\text{Area} &= \frac{1}{2} \times \textcolor{colordef}{10} \times \textcolor{colorprop}{12} \times \sin(\textcolor{olive}{50^\circ})\\
& \approx 46 \, \text{cm}^2\end{aligned}$$
Law of Sines
The Law of Sines relates the sides of a triangle to the sines of its angles. It is useful when we know two angles and one side (AAS or ASA) or one angle and two sides (SSA, which may have ambiguous cases).
Proposition Law of Sines
For a triangle with sides \(\textcolor{colordef}{a}\), \(\textcolor{colorprop}{b}\), \(\textcolor{olive}{c}\) opposite angles \(\textcolor{colordef}{A}\), \(\textcolor{colorprop}{B}\), \(\textcolor{olive}{C}\):$$\textcolor{colordef}{\frac{a}{\sin A}} = \textcolor{colorprop}{\frac{b}{\sin B}} = \textcolor{olive}{\frac{c}{\sin C}}$$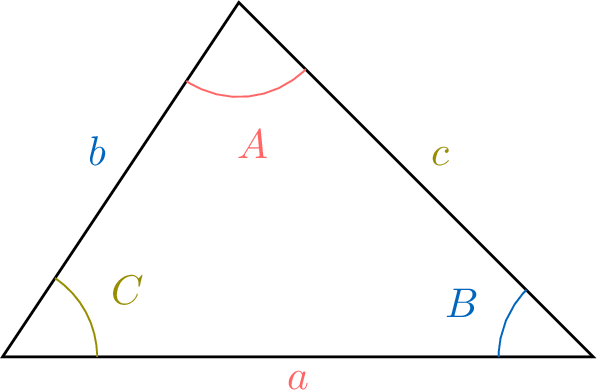

The area of the triangle can be expressed in three different ways using the formula \(\text{Area} =\frac{1}{2} \times \text{side} \times \text{side} \times \sin(\text{included angle})\):$$\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} bc \sin A = \frac{1}{2} ac \sin B = \frac{1}{2} ab \sin C.$$Diving each expressions by \(\frac{1}{2}abc\) gives:$$\ \frac{\sin A}{a} = \frac{\sin B}{b}= \frac{\sin C}{c}$$Thus,$$\frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B} = \frac{c}{\sin C}.$$
Example
For the triangle 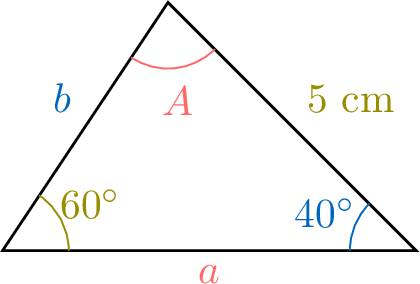 , find side \(a\).
, find side \(a\).
 , find side \(a\).
, find side \(a\).
First, find angle \(A\): \(A = 180^\circ - 40^\circ - 60^\circ = 80^\circ\).
Using the Law of Sines:$$\begin{aligned}\textcolor{colordef}{\frac{a}{\sin 60^\circ}} &= \textcolor{olive}{\frac{5}{\sin 40^\circ} }\\ a &= 5 \cdot \frac{\sin 60^\circ}{\sin 40^\circ}\\ a &\approx 6.73 \, \text{cm}\end{aligned}$$
Using the Law of Sines:$$\begin{aligned}\textcolor{colordef}{\frac{a}{\sin 60^\circ}} &= \textcolor{olive}{\frac{5}{\sin 40^\circ} }\\ a &= 5 \cdot \frac{\sin 60^\circ}{\sin 40^\circ}\\ a &\approx 6.73 \, \text{cm}\end{aligned}$$
Law of Cosines
The Law of Cosines is a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem for non-right-angled triangles. It is useful when we know three sides (SSS) or two sides and the included angle (SAS).
Definition Law of Cosines
For a triangle with sides \(\textcolor{colordef}{a}\), \(\textcolor{colorprop}{b}\), \(\textcolor{olive}{c}\) opposite angles \(\textcolor{colordef}{A}\), \(\textcolor{colorprop}{B}\), \(\textcolor{olive}{C}\):$$\textcolor{olive}{c}^2 = \textcolor{colordef}{a}^2 + \textcolor{colorprop}{b}^2 - 2\textcolor{colordef}{a}\textcolor{colorprop}{b} \cos \textcolor{olive}{C}\text{ and } \cos \textcolor{olive}{C} = \dfrac{\textcolor{colordef}{a}^2 + \textcolor{colorprop}{b}^2 -\textcolor{olive}{c}^2}{2\textcolor{colordef}{a}\textcolor{colorprop}{b}}$$Similarly for the other sides.

Example
For the triangle 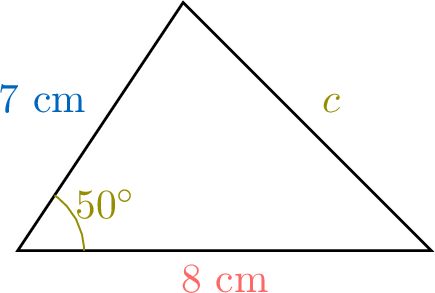 , find side \(c\).
, find side \(c\).
 , find side \(c\).
, find side \(c\).
Using the Law of Cosines:$$\begin{aligned}\textcolor{olive}{c}^2 &= \textcolor{colordef}{8}^2 + \textcolor{colorprop}{7}^2 - 2 \times\textcolor{colordef}{8} \times\textcolor{colorprop}{7} \times \cos \textcolor{olive}{50^\circ}\\
\textcolor{olive}{c}^2&\approx 41.0\\
\textcolor{olive}{c} &\approx \sqrt{41}\\
\textcolor{olive}{c} &\approx 6.4 \, \text{cm}\\
\end{aligned}$$
Solving Real-World Problems Using Sine and Cosine Laws
The Laws of Sines and Cosines are powerful tools for solving a wide range of problems involving non-right-angled triangles, especially in real-world contexts. To solve these problems effectively, follow the structured steps below:
Method Solving Real-World Problems Using Sine and Cosine Laws
- Draw a clear diagram representing the situation described in the problem.
- Label the known and unknown sides and angles in the triangle.
- Identify the configuration (e.g., two sides and included angle for Cosine Law, or two angles and a side for Sine Law).
- Choose the appropriate law (Sine Law for ratios of sides to sines of angles, Cosine Law for relating sides and cosine of an angle).
- Write and solve the equation to find the unknown value.